Solar-Powered Buses Are Revolutionizing City Transportation (Here’s How)
Imagine a future where city buses glide silently through streets, powered entirely by the sun’s energy. That future is already here. Solar-powered buses are revolutionizing public transportation by combining advanced photovoltaic technology with zero-emission mobility, offering a glimpse into sustainable urban transit solutions that work today.
These innovative vehicles represent a perfect fusion of renewable energy and public transportation, featuring rooftop solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity to power their electric motors. While traditional buses consume thousands of gallons of diesel fuel annually, solar buses harness free, clean energy from the sun, significantly reducing both operating costs and carbon emissions.
Cities worldwide are already experiencing the benefits of this groundbreaking technology. From China’s solar-powered fleet in Zhuzhou to Australia’s solar buses in Adelaide, these vehicles are proving that sustainable public transportation isn’t just an environmentalist’s dream – it’s a practical, cost-effective solution for modern cities committed to fighting climate change while keeping their residents moving efficiently.
How Solar-Powered Buses Actually Work
Solar Panel Integration
Modern solar panel technology seamlessly integrates into bus designs through innovative engineering solutions. The panels are typically mounted on the roof in a streamlined configuration that maintains the bus’s aerodynamic profile while maximizing sun exposure. These specially designed panels are lightweight, durable, and can withstand various weather conditions.
The integration process involves installing multiple photovoltaic panels across the bus’s roof surface, covering approximately 120-150 square feet of space. These panels are connected to power management systems that efficiently distribute electricity to the bus’s battery storage and operating systems. Anti-reflective coatings help maximize energy absorption while flexible mounting systems allow the panels to conform to the roof’s subtle curves.
To ensure optimal performance, manufacturers use high-efficiency monocrystalline or polycrystalline panels that can generate power even in partially shaded conditions. The panels are typically arranged in a series-parallel configuration, allowing the system to continue functioning even if individual panels are temporarily shaded or damaged. This thoughtful integration approach helps maintain the bus’s structural integrity while providing reliable solar power generation.
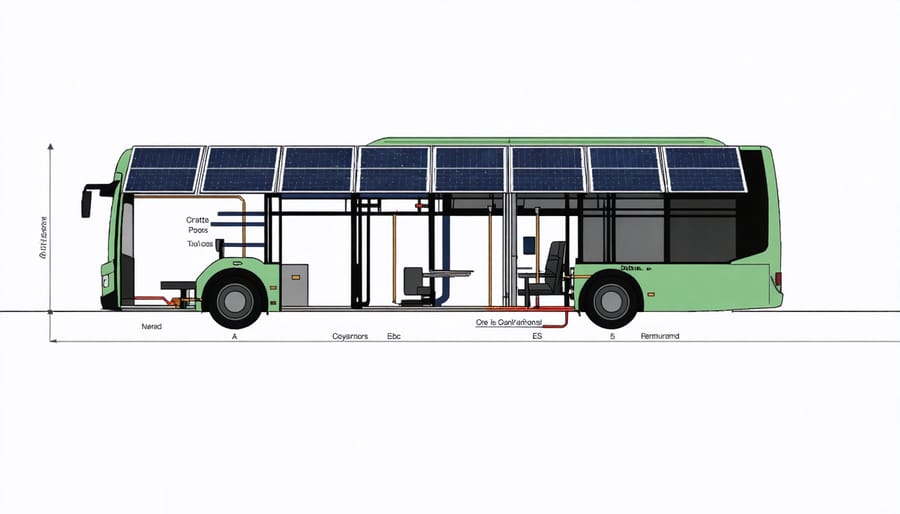
Energy Storage Systems
Solar-powered buses rely on advanced energy storage systems to maintain reliable operation throughout the day. At the heart of these systems are high-capacity lithium-ion batteries, specially designed to handle the demanding power requirements of public transportation. These batteries store energy collected from the rooftop solar panels during daylight hours and provide consistent power to the electric drivetrain.
Most solar buses employ a dual-battery configuration: a primary battery pack for regular operation and a backup system for extended range or cloudy days. Smart power management systems continuously monitor and optimize energy flow between the solar panels, batteries, and motor. This intelligent system ensures maximum efficiency by prioritizing solar power usage during daylight hours while maintaining battery health through controlled charging cycles.
The batteries typically have a lifespan of 8-10 years and can store enough energy to power the bus for 150-200 miles on a single charge. Modern energy storage systems also feature regenerative braking technology, which captures and stores energy normally lost during braking, further improving the bus’s overall efficiency and range.
Real-World Benefits of Solar Buses
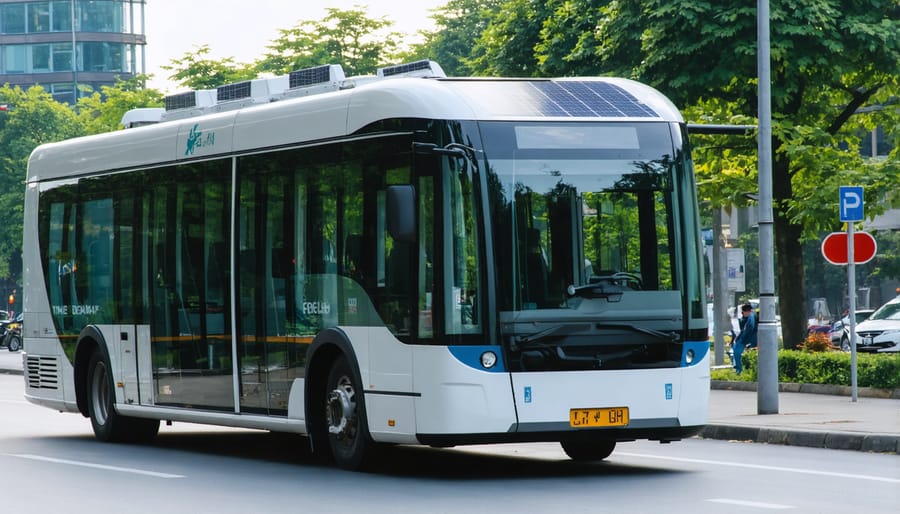

Environmental Impact
Solar-powered buses represent one of the most promising green transportation solutions available today, offering significant environmental benefits that extend far beyond reduced fuel consumption. A single solar-powered bus can prevent approximately 40 tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually compared to its diesel counterpart, equivalent to planting nearly 1,900 trees.
These eco-friendly vehicles dramatically reduce local air pollution in urban areas, eliminating harmful particulate matter and nitrogen oxides that traditional buses emit. The impact is particularly noticeable in densely populated cities, where air quality improvements can directly benefit public health.
The environmental advantages don’t stop at emissions reduction. Solar-powered buses contribute to noise pollution reduction, creating quieter, more livable urban spaces. Their solar panels can also be connected to the grid when the vehicles are parked, feeding surplus energy back into the system and supporting broader renewable energy initiatives.
From a lifecycle perspective, while the initial manufacturing of solar panels does have some environmental impact, the long-term benefits far outweigh these costs. Studies show that solar-powered buses reach their environmental break-even point within 3-4 years of operation, after which they continue to deliver positive environmental impacts for their entire service life, typically 12-15 years.
Cost Savings
Operating solar-powered buses brings substantial cost savings that benefit both transit authorities and taxpayers. The most significant advantage comes from reduced fuel costs, as these vehicles harness free solar energy instead of relying on expensive diesel fuel. Studies show that a single solar-powered bus can save between $8,000 to $12,000 annually in fuel costs alone.
Maintenance costs also drop significantly because electric motors have fewer moving parts than traditional combustion engines. Transit authorities report up to 40% reduction in maintenance expenses, as there’s no need for oil changes, fuel filters, or complex engine repairs. The solar panels themselves require minimal upkeep, usually just periodic cleaning and inspection.
Battery replacement costs, while initially a concern, have decreased dramatically in recent years. Modern lithium-ion batteries used in solar buses can last 8-10 years with proper management, spreading the replacement cost over a longer period. Many transit authorities recover their initial investment within 4-5 years through operational savings.
Infrastructure savings are another key benefit. Solar-powered buses can be charged using on-site solar installations at bus depots, reducing dependency on external charging stations. Some cities have implemented smart charging systems that store excess solar energy during peak production hours, further optimizing operational costs.
These combined savings allow transit authorities to invest in fleet expansion or improve other services while maintaining lower ticket prices for passengers.

Current Implementation Success Stories
Global Success Stories
Solar-powered buses have achieved remarkable success across the globe, demonstrating the viability of solar-powered transport vehicles in diverse climates and conditions. In Adelaide, Australia, the Tindo solar bus has been operating since 2013, serving thousands of passengers while producing zero emissions. The bus recharges at a central station powered by a massive solar panel array, proving that solar transportation can work effectively in urban environments.
China’s Zhuzhou City introduced a fleet of 50 solar-assisted buses in 2019, reducing the city’s carbon emissions by an estimated 120 tons annually. These buses utilize rooftop solar panels to power auxiliary systems, extending their range and reducing overall energy consumption.
Uganda’s Kiira Motors launched Africa’s first solar-powered bus in 2016, the Kayoola Solar Bus, showcasing how developing nations can leapfrog traditional transportation infrastructure. The bus can travel up to 80 kilometers on a single charge, making it perfect for urban routes.
In California, several school districts have embraced solar-electric buses, combining solar charging stations with electric vehicles. The Twin Rivers Unified School District reported a 80% reduction in energy costs after switching to solar-powered buses, while also creating cleaner air for students.
These success stories demonstrate how solar-powered buses are becoming a practical and sustainable solution for public transportation worldwide.
Lessons Learned
The implementation of solar-powered buses across various cities has revealed several valuable insights for future projects. First, the initial investment, while significant, typically pays off within 5-7 years through reduced fuel and maintenance costs. Cities that started with small pilot programs before scaling up have shown better success rates in managing the transition.
Weather adaptation has proven crucial, with many successful programs incorporating hybrid backup systems for cloudy days or extended night operations. This ensures service reliability while maintaining the primary benefits of solar power. Additionally, driver training programs have emerged as a critical factor, as operating these vehicles requires specific skills to maximize energy efficiency.
Public acceptance has been overwhelmingly positive, particularly when cities engage in community education about the environmental benefits. Passengers appreciate the quieter, cleaner ride, while operators report lower operating costs and reduced maintenance needs. The most successful implementations have also included strategic placement of charging stations and careful route planning to optimize solar exposure during operation.
Most importantly, these projects have demonstrated that solar-powered public transportation is not just environmentally responsible but also economically viable when properly implemented.
Future Developments and Possibilities
The future of solar-powered buses looks incredibly promising, with several exciting developments on the horizon. Manufacturers are working on next-generation solar panels that could increase energy efficiency by up to 40%, allowing buses to run longer routes without needing additional charging. These advanced panels will be lighter, more flexible, and better integrated into the bus design.
Battery technology is also evolving rapidly, with solid-state batteries expected to revolutionize energy storage in the next five years. These batteries will offer faster charging times, longer lifespans, and improved safety compared to current lithium-ion systems.
Cities worldwide are showing increased interest in solar bus programs, with many planning to convert their entire fleets by 2030. Smart city integration is another exciting possibility, where solar buses will communicate with traffic systems and charging stations to optimize routes and energy usage.
Emerging vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology will allow solar buses to serve as mobile power stations, feeding excess energy back into the grid during peak demand periods. This feature could help stabilize local power networks and generate additional revenue for transport operators.
Research is also underway to develop self-cleaning solar panels and regenerative braking systems that could further improve efficiency. With continued investment in renewable transportation, solar-powered buses are set to become a cornerstone of sustainable urban mobility.
Solar-powered buses represent a significant leap forward in sustainable public transportation, offering a glimpse into a cleaner, greener future of urban mobility. As cities worldwide embrace this technology, we’re seeing remarkable reductions in carbon emissions and operational costs. The success stories from places like Adelaide, Australia, and Santiago, Chile, demonstrate that solar-powered buses are not just environmentally friendly but also economically viable.
Looking ahead, experts predict widespread adoption of solar buses across major cities by 2030, driven by improving technology and decreasing costs. With enhanced battery storage capabilities and more efficient solar panels being developed, these vehicles are becoming increasingly practical for diverse climate conditions and routes. As we continue to face climate challenges, solar-powered buses stand as a shining example of how innovative transportation solutions can help create more sustainable cities for future generations.











