Solar Panel Manufacturing: The Environmental Impact You Need to Know
Solar panel manufacturing’s environmental impact presents a complex trade-off that every clean energy advocate must understand. While solar panels significantly reduce carbon emissions during their operational lifetime, their production process raises important environmental considerations.
Manufacturing solar panels requires substantial energy, raw materials, and chemical processes that can generate hazardous waste and greenhouse gas emissions. A typical solar panel’s production creates about 40g of carbon dioxide per kilowatt-hour – yet this same panel will offset hundreds of times more emissions during its 25-30 year lifespan.
The good news? Solar manufacturing is becoming cleaner each year as facilities increasingly power their operations with renewable energy and implement advanced recycling programs. Modern production techniques now reduce water usage by 40% compared to a decade ago, while silicon waste recycling has reached efficiency rates above 85% in leading facilities.
For environmentally conscious consumers, understanding these impacts helps make informed decisions about solar adoption while supporting manufacturers who prioritize sustainable production methods.
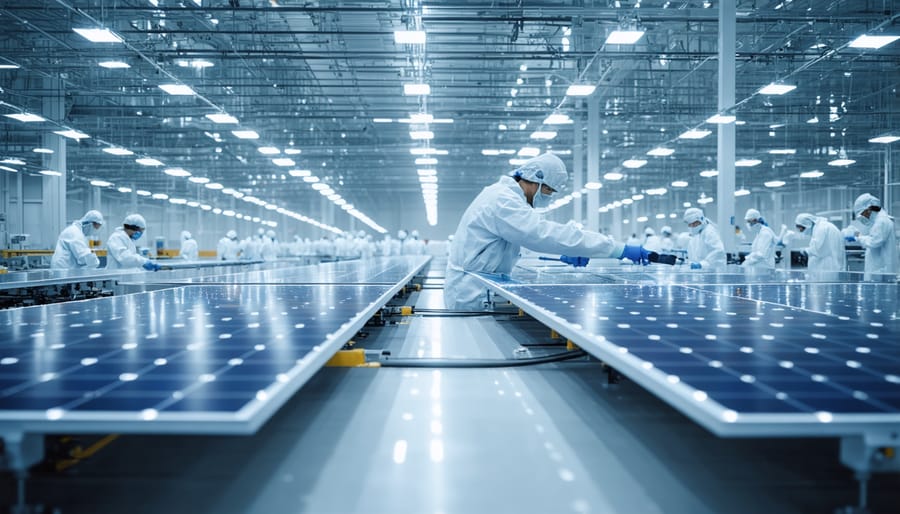

The Manufacturing Process and Its Environmental Footprint
Raw Material Extraction
The manufacturing journey of solar panel components begins with raw material extraction, a process that requires careful consideration of environmental impacts. Silicon, the primary material used in most solar panels, is derived from quartz mining operations. While abundant in nature, the extraction process involves substantial energy consumption and land disturbance.
Mining operations for other essential materials like silver, copper, and aluminum also contribute to the environmental footprint. These activities can lead to habitat disruption and require significant water usage. However, it’s important to note that these materials can be recycled effectively, reducing the need for new extraction over time.
The industry is actively working to minimize these impacts through sustainable mining practices and increased use of recycled materials. Many manufacturers now prioritize responsible sourcing and have implemented programs to reduce their environmental footprint. When compared to fossil fuel extraction, the long-term environmental benefits of solar energy still far outweigh the initial mining impact, especially considering that these materials create clean energy for decades after installation.
Chemical Processing and Energy Use
The manufacturing of solar panels involves several chemical processes and requires significant energy input, but manufacturers are continuously improving these methods to reduce their environmental impact. The primary energy-intensive step is the purification of silicon, which requires heating raw materials to extremely high temperatures – around 2,000°C. This process traditionally relies on electricity from the local power grid, though many manufacturers are now powering their facilities with renewable energy.
Chemical processing includes the use of hydrofluoric acid and sodium hydroxide for cleaning and texturing silicon wafers. While these chemicals require careful handling and disposal, modern facilities employ closed-loop systems that recycle up to 95% of these materials. Additionally, manufacturers are developing water-based alternatives and less toxic cleaning solutions.
The good news is that solar panels typically generate enough clean energy within 1-4 years to offset the energy used in their production. As manufacturing techniques advance and more facilities switch to renewable energy sources, this “energy payback time” continues to decrease, making solar panels increasingly environmentally friendly from production to installation.
Key Pollutants and Their Environmental Impact
Air Emissions
While solar panel manufacturing does produce air emissions, it’s important to understand the bigger picture. The primary greenhouse gases released during production include carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, mainly from the energy-intensive processes required to purify silicon and create solar cells.
The good news is that these emissions are significantly offset once solar panels are in operation. A typical solar panel will prevent 30 times more emissions during its lifetime than were created during its manufacture. Modern factories are also implementing cleaner production methods and increasingly using renewable energy to power their operations.
Chinese solar manufacturers, who produce the majority of the world’s panels, are making substantial progress in reducing their carbon footprint. Many facilities now use advanced filtration systems and scrubbers to minimize harmful emissions. Additionally, several leading manufacturers have committed to powering their production facilities with 100% renewable energy by 2030.
For perspective, the air emissions from solar panel manufacturing are far lower than those from traditional energy sources like coal or natural gas power plants, making solar a significantly cleaner choice for our environment.
Water and Soil Contamination
Water plays a crucial role in solar panel manufacturing, particularly in the production of silicon wafers and the cleaning of materials. While the industry has made significant strides in reducing water consumption, the process still requires substantial amounts of purified water. Modern facilities typically implement advanced water recycling systems, helping to minimize their overall water footprint.
During manufacturing, there’s potential for chemical substances used in the production process to affect local water sources if not properly managed. However, strict environmental regulations and industry best practices help ensure proper handling and disposal of these materials. Many manufacturers now use closed-loop water systems that treat and reuse water multiple times before disposal.
Soil contamination concerns primarily arise from improper disposal of manufacturing byproducts or damaged panels. The good news is that leading manufacturers have developed comprehensive recycling programs and waste management protocols. These initiatives help prevent harmful materials from reaching the soil and ensure responsible end-of-life handling of solar components.
It’s worth noting that the solar industry continues to innovate, developing new manufacturing techniques that reduce water usage and minimize environmental impact. Many facilities now operate under zero-liquid discharge policies, demonstrating their commitment to environmental stewardship while producing clean energy technology.
Industry Solutions and Progress
Cleaner Manufacturing Technologies
The solar manufacturing industry is making remarkable strides in reducing its environmental footprint through innovative production methods. Leading manufacturers now use closed-loop water recycling systems that reduce water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional manufacturing processes. These systems capture, filter, and reuse water multiple times before it needs replacement.
Another significant advancement is the adoption of energy-efficient furnaces that use renewable energy for silicon melting and purification. Some facilities now power their manufacturing operations entirely with solar energy, creating a sustainable cycle of clean energy production.
Manufacturers are also implementing chemical recycling programs that recover and reuse valuable materials like silicon tetrachloride, significantly reducing waste and toxic emissions. Advanced robotics and automation have improved production precision, resulting in fewer defective panels and less material waste.
Recent innovations in panel design allow for easier end-of-life recycling. New manufacturing techniques create panels that can be disassembled more efficiently, making it possible to recover up to 95% of valuable materials. Some companies now use lead-free soldering methods and have eliminated toxic chemicals like cadmium from their production processes.
These cleaner technologies not only benefit the environment but also reduce production costs, making solar panels more affordable while maintaining high efficiency standards. As these manufacturing improvements continue to evolve, the solar industry is becoming increasingly sustainable throughout its entire lifecycle.
Recycling and Waste Reduction
The solar industry is making significant strides in addressing manufacturing waste through innovative recycling programs and waste reduction initiatives. Today’s solar panels are approximately 95% recyclable, with manufacturers implementing closed-loop systems to recover and reuse valuable materials like silicon, glass, and aluminum.
Leading solar companies have established dedicated recycling facilities that specifically handle end-of-life panels. These facilities employ advanced separation techniques to extract precious metals and semiconductor materials, which can then be repurposed for new panel production. This recycling process not only reduces waste but also decreases the energy required for manufacturing new panels.
Proper solar panel maintenance plays a crucial role in extending panel lifespan and reducing waste. Well-maintained panels can last 25-30 years, significantly lowering their environmental impact over time.
Many manufacturers now utilize eco-friendly packaging materials and have optimized their production processes to minimize waste. Some companies have introduced take-back programs, accepting old panels for recycling when customers upgrade their systems. Additionally, industry regulations are becoming stricter, requiring manufacturers to implement sustainable practices and proper disposal methods.
Looking ahead, emerging technologies promise even more efficient recycling methods, including automated dismantling systems and chemical processes that can recover up to 99% of raw materials from old panels.

Making an Informed Decision
When considering solar panel installation, it’s essential to weigh both the environmental impacts of manufacturing and the long-term benefits of clean energy production. While the manufacturing process does create some pollution, most solar panels offset their carbon footprint within 1-4 years of operation, then continue producing clean energy for decades.
Modern manufacturing techniques are continuously improving, with many companies now using renewable energy to power their production facilities and implementing closed-loop recycling programs. This progress, combined with stricter environmental regulations, has significantly reduced the industry’s overall environmental impact.
The key to maximizing environmental benefits lies in choosing high-quality panels from manufacturers with strong sustainability practices. Look for companies that provide transparency about their manufacturing processes and have clear end-of-life recycling programs. Additionally, combining solar installation with improved home energy efficiency can further reduce your environmental impact.
Remember that while manufacturing impacts are important to consider, solar energy remains one of our most promising solutions for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and fighting climate change. The technology’s rapid advancement means newer panels are more efficient and environmentally friendly than ever before, making solar an increasingly positive choice for both homeowners and the planet.
While solar panel manufacturing does create some environmental impacts, the long-term benefits far outweigh these initial challenges. Today’s solar panels typically offset their manufacturing emissions within 1-3 years of operation, while continuing to provide clean energy for 25-30 years. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting cleaner production methods, using recycled materials, and developing more efficient panels that require fewer resources to produce. As the industry continues to evolve, we’re seeing remarkable improvements in both manufacturing processes and panel efficiency. The shift toward solar energy remains one of our most powerful tools in combating climate change, reducing air pollution, and creating a sustainable future for generations to come. By choosing solar, you’re contributing to a cleaner energy landscape while enjoying significant energy savings and energy independence.











